

Cloud deployment models: Overview and comparison
Cloud computing accumulated more than $300 billion of global revenue in 2020, and there is little sign of a slowdown in the market. According to statistics, companies globally will be investing up to 110.5 billion US dollars in cloud-powered systems by 2024.
The increase in demand has led to the emergence of several varieties of cloud deployment models offering different rates of scalability, convenience, performance, privacy, and cost. Surely, it’s not always clear which one is more suitable for business. Possessing fundamental knowledge in these matters, DICEUS decided to tell in more detail about the main deployment models of cloud computing. We hope this will help you make the right choice.
What is cloud deployment?
Deploying an application today does not exclusively require physical infrastructure. Cloud services allow you to receive both a server and data storage that can be used for personal needs. Distributed systems combining the power of a large number of computers, grid computing, and virtualization ultimately provide more possibilities.
The cloud deployment model is the backbone of cloud system implementation. It is a diagram of how users interact with resources and network infrastructure located in different locations. It determines where the servers you use are located, who manages them, what you can change yourself, whether you provide services or have to build them yourself.
In essence, the shape and size of a model are dictated by the cloud infrastructure’s purpose and rate of availability.
Need cloud computing services? Check out our cloud solutions and services!
What cloud computing deployment routes are there?
The essential models differ in managing, owning, handling security protocols and access control specifics. Previously, only 4 deployment models of cloud computing used to be defined. Today, we have five schemes to tackle.
Public cloud
A public cloud is a free-use infrastructure or cloud hosting providing open access to systems and services. Vivid instances are Amazon EC2, IBM Cloud, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure, etc.
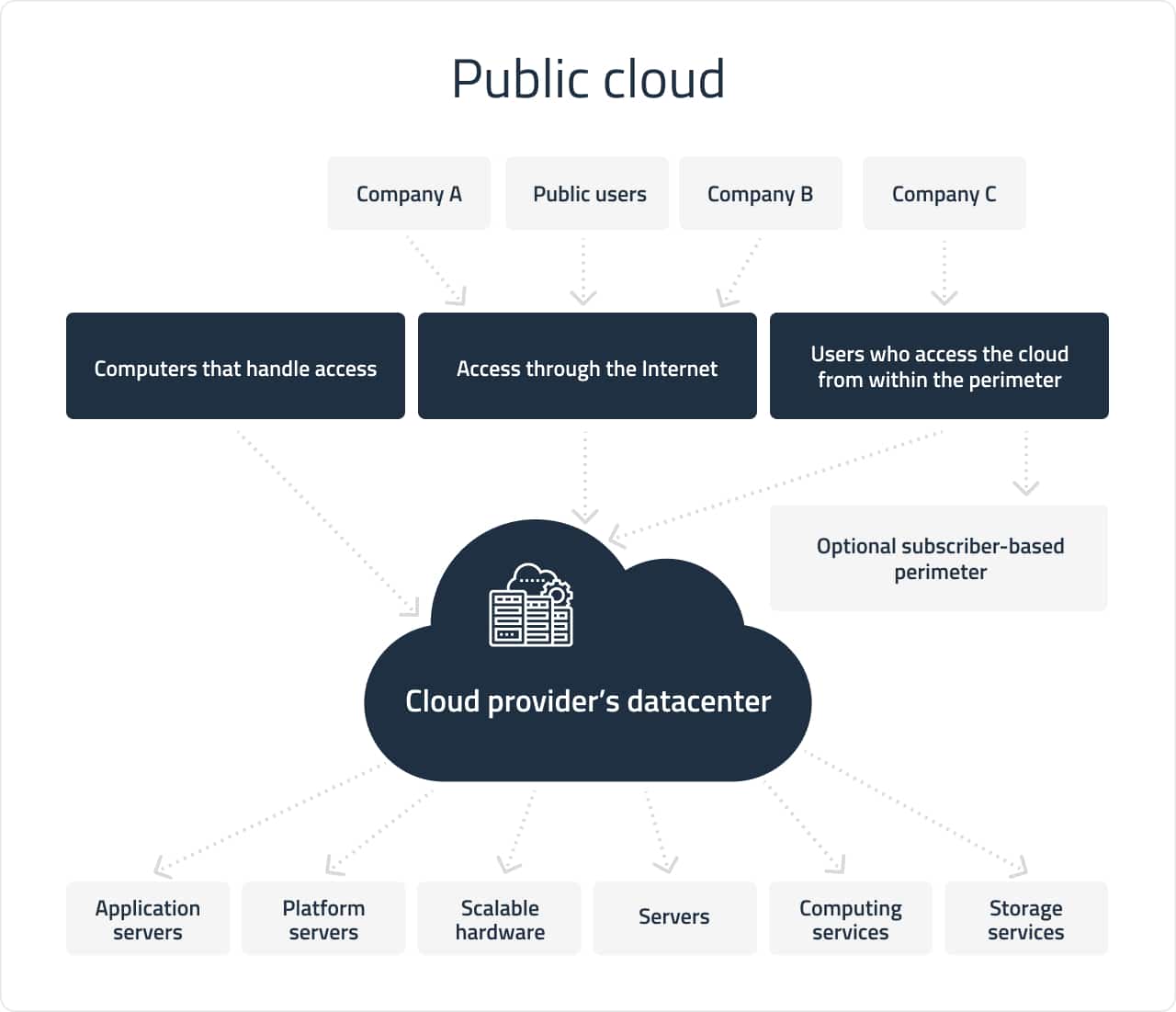
The infrastructure is owned by service providers, so there is no need for users to buy and maintain their own hardware. Vendors offer resources as a service with pay-as-you-go tariffs, all working online. And you can scale these resources as needed.
This is the best choice for businesses operating in low-privacy industries.
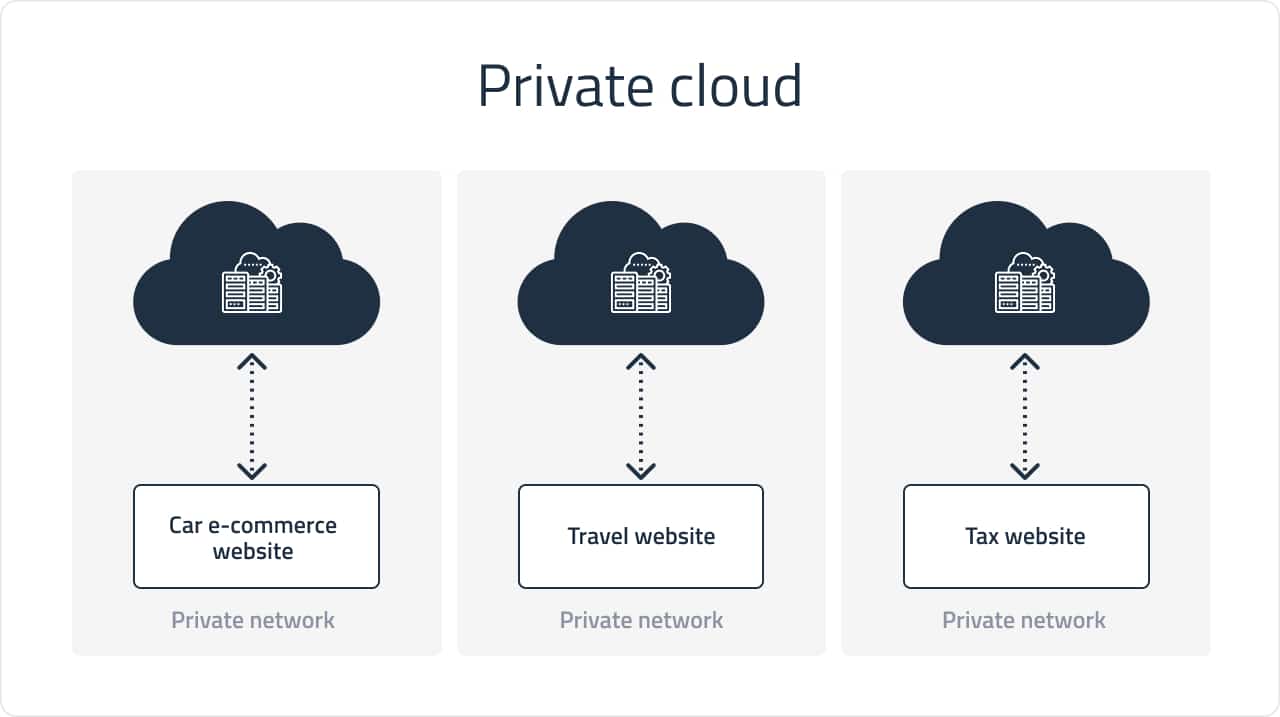
Private cloud
From a technical point of view, there is practically no difference with the public model. The defining nuance is that the private cloud system is used by only one organization. The systems and services are only made available to authorized users. The cloud has higher security standards and is controlled by the IT departments of the same company. It is a great solution for businesses with high data security requirements.
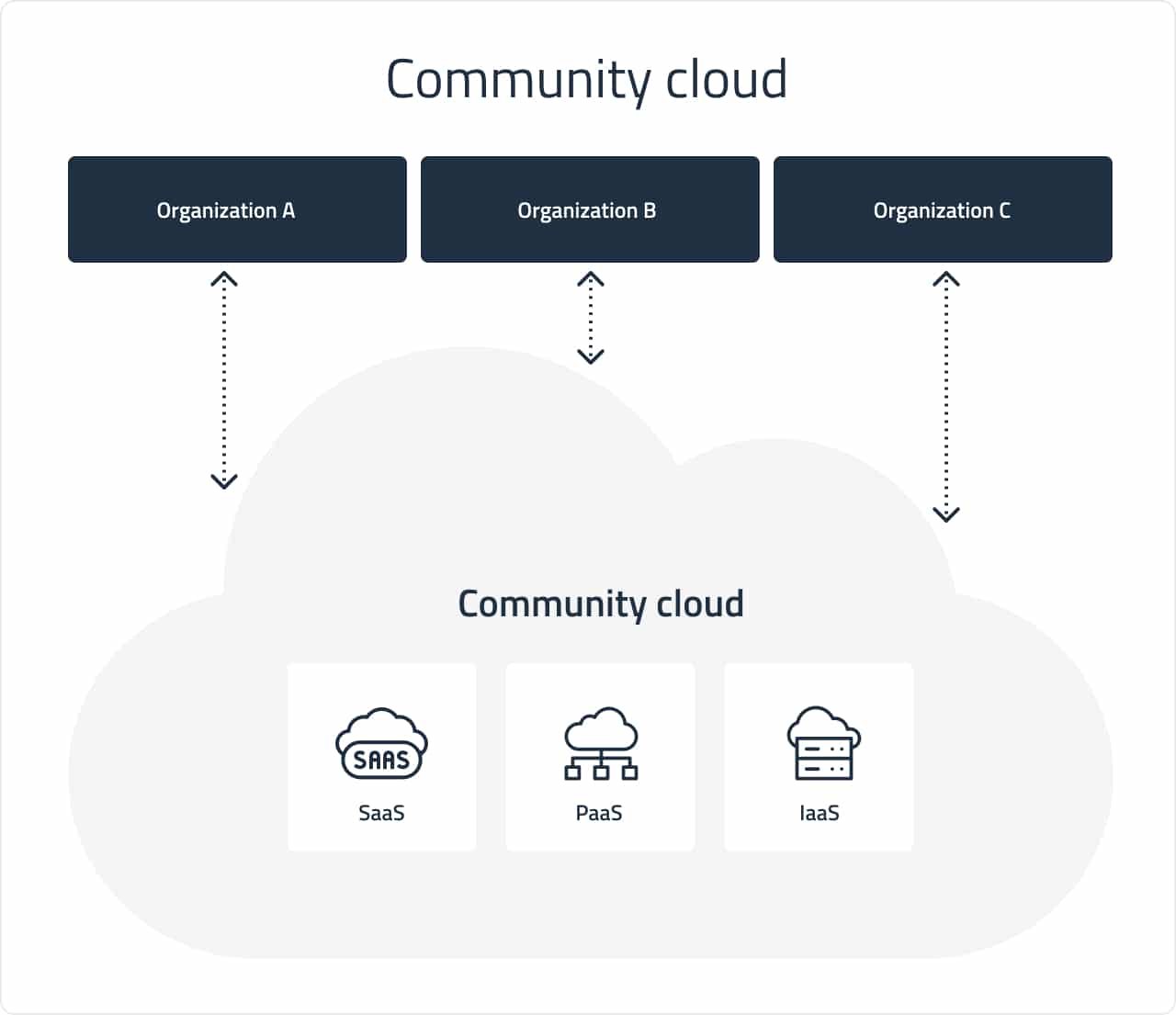
Community cloud
This is the infrastructure for use by a specific consumer community. The deployment model is very similar to the private one, however, not one organization owns the server and associated resources but several organizations that have similar or common computational tasks — for instance, banks, joint business projects, etc.
Hybrid cloud
Given the type of cloud deployment model combines multiple cloud servers of different types, integrating them into one architecture but leaving them as separate entities.
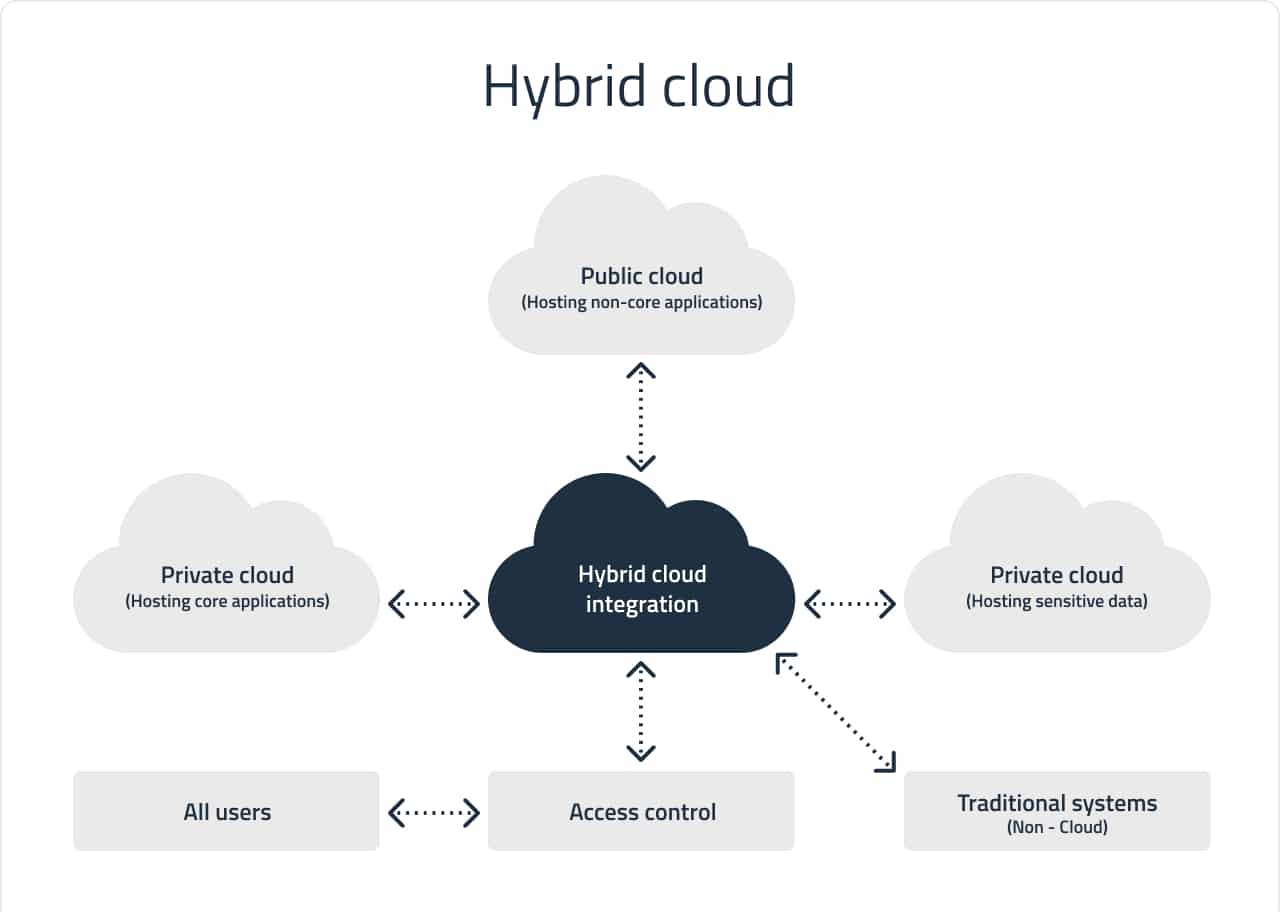
Secondary tasks, including the analysis of development and testing workloads, can be handled using the public system. The hybrid cloud approach protects and controls strategic assets in the most cost-efficient manner. On top of that, this model simplifies and streamlines the transfer of data and applications.
Multi-cloud
Multi-faceted deployment models employ solutions from several cloud providers at once. This is similar to the hybrid models but allows for multiple public cloud resources. Ideal for redundancy, provide higher availability of services and services from different clouds.
Comparing cloud deployment models
Specific types of cloud deployment models provide variability in use. For example, for various reasons, some companies are more suitable for public clouds. In contrast, others do not want to use them due to the complexity, secrecy of projects, or legislation requirements on the protection of intellectual property rights.
In order to pick the best fitting model, start by identifying your specific requirements:
- Ease of configuration: public, community, and multi-cloud platforms are the best in this aspect as most of the work is done by the ISP.
- Ease of use: public and multi-cloud are the best in this regard, hybrid is also suitable with the right system settings.
- Data control: These capabilities are more in-depth in private, hybrid, and public clouds when community members collaborate.
- Reliability: Highest in a private cloud. A hybrid can have a sufficient level if it is well-tuned.
- Scalability: Private and hybrid clouds provide the greatest capabilities here.
- Security and confidentiality: the highest level is distinguished by private, public (if participants adhere to corporate security policy), and hybrid cloud.
- Flexibility: the best options here are private and hybrid clouds since no one bothers you to settle resources.
- Cost: The most inexpensive solutions are public and community clouds because the cost is shared between users.
- Hardware requirements: Public and community clouds, by definition, require nothing here.
A public cloud is a standard case scenario for small- to medium-scale businesses. The larger the organization, the more important it is to a private cloud. For large enterprises wishing to minimize costs, it is worth choosing trade-offs.
Three service models of cloud computing
Despite the different types of cloud deployment models, no matter how you configure and manage equipment, you can pick from several basic service models:
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
You don’t have to choose a single service model. You can pick different ones for different cloud infrastructure components.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
With this cloud service model, you sort of rent the necessary hardware (servers, storage space, and dedicated network) managing only the software it is hosting. I.e., you get a ready-to-use virtual machine equipped with the operating system you require, full software access, and control. You are probably familiar with this approach if you have used Azure, AWS, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Google Cloud, etc.
The ultimate advantages of this choice are simplicity and flexibility. The virtual machine quickly gets up and running. You can reinstall the OS, install any custom software, virtually clone any existing IT infrastructure, creating disaster recovery solutions.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Here, you do not control the operating system and the software installed on it. The provider does this. In this model, you are not limited to one specific application, but you can only operate within one platform. Installing and configuring a Kubernetes or Kafka cluster can take several hours. With PaaS, you can get it done in minutes. However, since the provider controls the platform, you may not be able to get a unique configuration.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
This way of cloud computing deployment provides a higher level of abstraction. The service provider manages virtually every layer of the cloud infrastructure. The difference with PaaS is that you are limited to a specific application. On the other hand, you can deploy a MySQL database and start writing data to it in a matter of minutes. You get a platform that does nothing by itself, on which you create something that works. The downside is that SaaS services are slightly more expensive.
DICEUS expertise
Only a deep understanding of the goals will make it possible to solve complex problems. At DICEUS, we develop cloud-based applications that enable customer organizations to leverage resources regardless of geographic location. Our solutions accelerate time-to-market, lower costs, and increase operational efficiencies by rapidly deploying cloud and IT infrastructures.
The company also offers consulting services and analyses to identify business-enhancing operations and technologies. We have experience in creating and implementing customized solutions from scratch for developing cloud applications and migrating virtual servers using different models for deployment in cloud computing.
Need consulting on cloud technology? Check out our services.
Benefits we bring
As preliminary research, we study in detail the business model and determine the readiness for implementation in the cloud or migration to another platform. We collect functional and non-functional requirements to provide a solution that meets customer expectations and business needs. Thorough preparation includes steps toward developing the right strategy and making recommendations for implementing the project.
We create and implement SaaS software such as ERP, CMS, and HRM with a predetermined number of modules and functionality. Our best practices may include re-hosting, refactoring, and combining applications and clouds. We guarantee:
- lower IT management costs
- higher flexibility of processes
- no business downtime
- effective collaboration
With our deployment models for cloud computing, your employees can keep in touch with customers from anywhere at any time. They will also become more flexible in making decisions. Managing your big cloud data reliably and continuously will enable you to create and share reports faster with stakeholders. All this will greatly increase the attractiveness of your brand in the eyes of both customers and partners.





