ERP for banks: Benefits, custom vs. out-of-the-box solutions, tips on choosing
With constant modernization and digitization, present-day businesses realize the importance of proper software solutions to efficiently manage their operations, people, and customers. Even medium and small companies implement such products, not to mention large corporations. Currently, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems represent the most popular approach to maintaining in-house business processes, gathering, storing, and interpreting data. Having emerged as manufacturing software, the applications mentioned are now widely used in every modern industry. The banking sector is continuously growing and adopting ERP systems. ERM in banking helps automate core processes like account management, payments and transfers, risk management, customer support, and regulatory compliance.
Financial facilities require a high level of security and streamlined, reliable workflows that prevent even the smallest potential errors. If you consider the possibility of deploying ERP for your company, it’s better to clarify definitions and features so you can choose the best product. We will begin with some general data and then move to unique stuff related to banks.
Need a custom ERP system? Learn more about our services.
ERP definition, origin, and expansion
It’s not an easy task to define what ERP is exactly because this marketing term consists of two parts:
- A strategy. Here, ERP is a managerial approach to organizing core processes inside the company’s internal system.
- An application. ERP is a category of software that helps to enforce the strategy.
Simply put, the current conception of ERP recognizes it as an information system to store and process large packages of crucial company data. Hence, ERP software for banking industry focuses on key processes such as financial transactions, protecting clients’ sensitive info, connecting multiple departments, etc. It’s important to note that such solutions barely can handle literally all business tasks because this leads to great implementation costs and difficulty. Thus, you should define the essential things to gather them into a single solution. Our company can help with this stage by providing a comprehensive business analysis.
The basic idea behind ERP was introduced by the Gartner Group in 1990. The first solutions were designed to manage manufacturing processes using actual software. Due to the Y2K problem, many companies decided to replace their outdated platforms with ERP in the late 1990s. While traditional products were focused on back-office tasks, further development introduced front-office features of ERP: e-commerce practices, communication with clients, and CRM apps. In the XXI century, web ERP for banking industry and other sectors appeared to facilitate the collaboration of different enterprises via the Internet.
DICEUS has more than 13 years of experience in developing software for banks. Learn more!
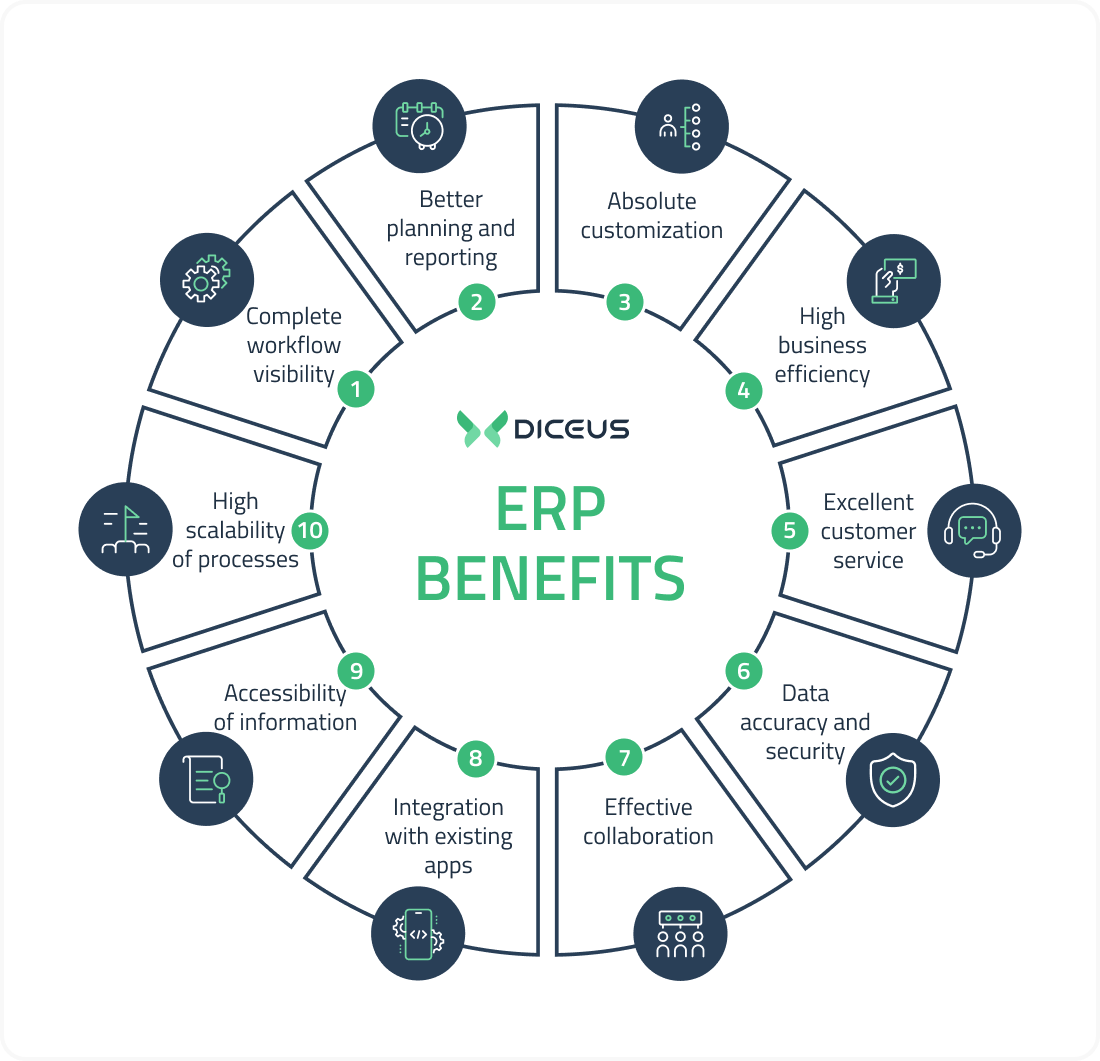
Why banks need an ERP: Benefits of using ERP for banking
So, why do banks need ERP systems? Here are the top advantages of banking ERP solutions.
Benefit 1 — Access to real-time data
An ERP system in banking provides access to real-time data by integrating various processes and functions across the organization into a centralized data repository. The data from various sources like customer accounts, loans, investments, and deposits are incorporated into a single database where the data is stored up-to-date and is accessible in real-time. Besides, modern ERP in banking sector can capture data, minimizing or eliminating manual data entry and reducing the likelihood of errors. Access to real-time data provides banks with a single source of truth and accurate information for analytics and reporting.
Benefit 2 — Improved security
Data security is paramount in banking. Enterprise resource systems protect important financial data with strong measures such as role-based access control, data encryption, data masking, firewalls, and regular data security updates. These measures prevent unauthorized access, detect unusual and fraud-like activities, and ensure disaster recovery and business continuity.
Benefit 3 — Advanced CRM
It is also important that banking software has some modules for customer relationship management. Typically, ERP for financial organizations has CRM modules, allowing banks to segment customers, gather and analyze customer feedback, forecast customer needs, and more. Thanks to access to real-time analytics, banks can create personalized offerings, improve customer experience, and predict sales and revenue.
Benefit 4 — Streamlines efficiency
By implementing a custom ERP system, banks can optimize their workflows thanks to centralized data management, automated processes, enhanced decision-making and customer support, and integration with third-party solutions. For example, by implementing a chatbot, banks provide their customers with a convenient communication channel that instantly responds to their questions and inquiries. So, customers are more satisfied, whereas banks can reduce customer support costs.
Basics of ERP software for banking industry
Similarly to other companies, financial corporations began implementing ERP apps in the early 2000s. Now, some banks use basic systems with slightly modified modules, but more businesses migrate to customizable products that suit current demands for security, data processing, and money control. Banking consists of exclusive customer-related activities such as deposits/credits, cash transactions, and digital money flow, so facilities have to build their reputation to attract and retain clients. Faults are simply unacceptable.
Further, we want to cover the major features of ERP software for banking industry: characteristics and modules.
Necessary characteristics
To start with, let’s look at the key operational principles of decent apps. They must be:
- Integrated. A single database and working ecosystem should include the chosen core business processes regardless of the company’s complexity. Thus, ERP helps big banks to gather valuable data with simplified subsequent processing and analysis.
- Unified. Respectively, local or web ERP for banking industry should smoothly work with different applications. Ideally, every bank’s branch has quick access to the global ERP solution, so local and chief managers can easily track performance.
- Real-time. The fast-changing finance sector requires an equally fast response from institutions. During financial crises, banks with quick reactions can cut insane losses while sluggish ones can be destroyed.
- Multilanguage and multicurrency. This part is extremely essential for transnational financial enterprises. Good solutions support several accounting and tax schemes, currencies, languages, etc.
Additionally, the most traditional approach to ERP for the banking industry provides ready-made replicable solutions. In other words, developers prefer to create universal systems that suit various organizations with different preferences and extensions. Replicable ERP software is convenient because it allows the integration of best practices.
However, banks may require unique custom platforms for managing and protecting sensitive data. Our team deploys tailored solutions for different enterprises, including financial ones, because we prefer a personalized approach with solid analysis. We are more technology partners rather than outsourced developers, so we guarantee quality and timeliness.
ERP modules
Regardless of the chosen product type (premade or custom), you will get a system that consists of several modules. Usually, ERP software for banking industry also features these parts. Some of them are core and obligatorily, while others are switchable elements that you can enable or disable independently. Traditional ERP is based on its platform divided into:
- Core. The framework acts as a foundation for extensions and includes APIs, codes, and data processing methods.
- Functionality. The underlying tools that are necessary for all companies. This part can’t be disabled like more specialized elements.
Over the platform, there are modules. Earlier, ERP for banking industry featured a lot of tools, including CRM, PPM, PLM, and so on. Nowadays, they come as separate solutions integrated for an extra price. Hence, modern ERP covers more internal processes and tasks rather than communications with clients. Modules are divided into the following parts:
- Finance. Banks are interested in the general ledger, debit and credit accounts, and tools for managing cash flows, liquidity, investments, and risks.
- Staff. This category is pretty universal for any company as it facilitates employees’ hiring, training, evaluation, and compensation.
- Operations. The most valuable part is that it delivers core services. Banks need the proper processes for manufacturing, planning, and distributing their business.
Apart from this classification, general ERP elements may be for inner use (designed for employees: accounting, manufacturing) and for external use (designed for clients: CMS, personal profiles). Finally, there are connectors that care about the interaction between ERP and non-ERP systems used in the enterprise.
The overall scheme may look a bit complicated, but remember that you can add and remove everything when you order a customized local or web ERP for banking industry. Even the basic functionality can be easily modified according to the bank’s goals and needs.
You might be interested in reading this article: “Master data management (MDM) in the banking sector: Challenges and benefits”
Pros and cons of ERP solutions
First and foremost, ERP is the way to combine all essential business processes in a single powerful system. There are tons of advantages, so check the most valuable ones that are perfect for banks:
- Easy access to financial data. It’s enough to input information once to make it available for everyone with permission. Such data come without extra revision.
- Communication between branches. ERP software for banking industry connects all departments and greatly facilitates workflow.
- Control and monitoring. While everything is tracked by machines, it becomes really simple to check staff performance or business processes’ current states.
- Fewer human-related errors. The global ecosystem eliminates the possibility of missing transactions, forgotten accounts, or technical distortions.
On a par with strengths, there are always some weaknesses. They are strongly linked with advantages and, thus, are inevitable:
- Dependence on hardware. Stand-alone products can’t work without solid servers. However, SaaS web ERP for banking industry is less demanding.
- A complicated system of permissions. Banks have to control security and create different access levels for different employees. It may be difficult for large corporations.
- High implementation and switching costs. Again, a fully functional ERP with many modules is expensive, as you have to install it and train workers.
Tips on choosing ERP software for banking industry
To start with, there are numerous developers of ERP applications. The majority of leading companies focus on ready-made solutions that feature best practices suitable for any industry. If you are ready to work with a predefined set of tools and modules, pay attention to teams like SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft.
Some notable banking corporations rely on the described preprogrammed solutions. Just take a look:
- Standard Chartered (the UK, 86,000 employees) – SAP ERP.
- APG Groep N.V. (Netherlands, 4,000 employees) – SAP ERP.
- Customers Bank (the USA, 822 employees) – FIS Global ERP.
- Bankrate (the USA, 384 employees) – NetSuite ERP.
- Columbus Capital Landing (the USA, 195 employees) – Ellie Mae ERP.
- Arquia Banca (Spain, 170 employees) – SAP ERP.
How custom solutions overcome ready-made alternatives
The problem of the aforementioned examples is hidden in the generalization. Ready solutions are poorly customizable because each unusual module imposes additional costs. That means that tailor-made products are more efficient because they feature only the necessary functions and are developed for your company exclusively.

| Aspect | Custom ERP systems for banks | Ready-made solutions |
| Development time | Longer development time due to customization | Faster implementation as it’s a pre-built solution |
| Customization flexibility | Highly customizable to meet specific needs | Limited customization options |
| Initial cost | Higher initial investment due to development | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance and support | Requires ongoing maintenance and support | Typically includes maintenance and support |
| Scalability | Can be scaled according to the bank’s growth | May have limitations on scalability |
| Integration with existing systems | Integration can be complex but highly tailored | Often designed for seamless integration |
| Compliance and regulation | Can be customized to meet specific regulations | Compliance features built-in, but less flexible |
| Implementation risks | Higher risk due to customization complexity | Lower risk as it’s a pre-built solution |
| Training requirements | More extensive training for unique features | Training is often standardized for all users |
| Long-term cost | Higher long-term costs due to maintenance | Lower long-term cost due to standardized model |
Before ordering a custom ERP solution, be sure to consider the following points:
- Key goals of the software. Define what exactly the launched app will handle. Banks should be interested in controlling financial flows, accounting, protecting the customer’s sensitive data, and connecting different branches in a single network.
- The company’s core processes. Similarly, remember your business processes. For example, small banks can order a simple basic ERP with accounting/cash management tools, while transcontinental enterprises will need various tax rules, currencies, and departments.
- Platforms to work on. Think about how applications will be deployed. Companies usually order stand-alone or SaaS solutions for launching on desktop clients. Sometimes, you will need mobile applications for more flexible control.
- The budget. Finally, ensure that you can afford to spend enough money. Sometimes, clients want large functional packages when they actually don’t need some of their features. For this, we launch an MVP to show how tech works.
What are the primary questions to ask yourself about providers
After you are done with the previous stuff, proceed to the final stage and choose a team that will develop and integrate the product. Be sure to find developers who will be able to launch the most suitable ERP for your business. For this, we recommend asking yourself a few questions that should facilitate the selection process:
- Are developers experienced? Look for teams that have enough knowledge in the chosen industry. To evaluate vendors, you can look at their previous projects: ones with positive client reviews and proven efficiency are successful.
- How do developers organize their work? Companies that utilize the Agile methodology and deliver MVPs before charging the full cost of ERP deserve your attention. It’s better to ask about these processes personally to avoid miscommunications.
- Which technologies do they use? For example, .NET, Python, and Java are best practices for back-end solutions, while Angular and jQuery are good for the front end. Additionally, developers should have knowledge of SQL, Azure, and Oracle.
- On which pricing model are they focused? Hourly rates are typical for freelance developers, but advanced outsourcers prefer to quote prices that are set for each project independently. Thus, you can be sure that no hidden fees will be added further.
Our company has extensive experience in creating ERP systems for various teams, including banks. We have some use cases with leading national and global companies for which we have designed and launched:
- Comprehensive data warehouses with end-to-end flows featuring basic tools like general ledgers and more advanced options such as business rules or COTS systems.
- Online banking applications for mobile gadgets through which customers can access their wallets and transactions. We also have worked on bigger projects for web systems with the implementation of personal accounts, credits/deposits, and currency exchanges.
- FinTech systems based in the cloud or deployed on clients’ servers. These projects were focused on accounting, analytics, and data visualization with a high level of automation.
Related article: “Data governance for banks: Top 5 benefits of implementing”
Your perfect ERP
If you are considering the implementation of ERP for your bank, feel free to contact our team for a first consultation. We will provide all the detailed info about our ERP software versions for the banking industry, the whole development process, and important things for your business exclusively.
FAQ
What is ERP, and how does it apply to the banking industry?
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, refers to software systems that integrate and optimize various business processes within an organization. In the banking industry, ERP systems play a crucial role in managing financial operations, customer relationships, loan processing, transaction handling, compliance, risk management, and human resources. By centralizing data and automating key processes, ERP systems enable banks to improve efficiency, enhance customer service, ensure regulatory compliance, and make informed decisions. These systems facilitate seamless operations, reduce manual effort, and provide real-time visibility into critical business data, thereby helping banks adapt to changing market conditions and drive sustainable growth.
What are the key modules typically included in ERP for the banking industry?
ERP systems for the banking industry typically include key modules such as accounting and financial management, customer relationship management (CRM), loan management, transaction processing, compliance and risk management, and human resources management. These modules enable banks to streamline core banking operations, manage financial transactions, track customer interactions, automate loan processing, handle regulatory compliance, and optimize workforce management. Additionally, ERP systems may incorporate modules for supply chain management, business intelligence, and analytics to further enhance operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities within banks.
Can ERP for the banking industry support multiple banking channels?
Yes, ERP systems for the banking industry can support multiple banking channels by providing integration with various delivery channels such as branches, ATMs, online banking platforms, mobile banking apps, and call centers. These systems enable seamless communication and data sharing between different banking channels, ensuring consistency in customer experience and transaction processing across all touchpoints.
Is ERP for the banking industry customizable to suit the unique needs of different banks?
Custom ERP systems for the banking industry are fully customizable to suit the unique needs of different banks.